(A) Mass-Flow/Pressure Flow Hypothesis:
1. The mass-flow/pressure flow hypothesis:
- postulates that dissolved sugar moves in phloem
- by mean of pressure gradient
- which exists between the source and sink.
2. The photosynthetic cells in:
- leaves = common source of sugars - roots = sinks.
3. At the leaves
- sucrose is actively transported
- from mesophyll cells
- to companion cell
- into sieve tube
- against its concentration gradient
- process = phloem loading.
- high conc of sucrose↑ à lowers cell water potential (Ψw)↓.
- water - drawn into sieve tube
- from nearby xylem vessel
- creating a high hydrostatic pressure (HP)↑
- forces the bulk/mass flow of the phloem sap
- towards the sink.
4. At the root:
- sucrose is actively transported
- from the sieve tube
- into the companion cell
- into a root cell.
- process = phloem unloading.
5. Loading (at the source) and unloading of sugar (at the sink)
- require energy derived from ATP.
(B) In Electro-Osmosis Mechanism:
- potential diff develops across sieve plate
- by companion cell (actively transport K+ into sieve tube).
- K+ accumulate at one end of sieve plate
- creates a potential diff between sieve plate.
- caused K+ speed across sieve plate
- water + dissolved sucrose follow (attracted by +ve charge).
- water in phloem moves by osmosis
- as accumulation of K+ lower Ψw in sieve tube (compared to next cell).
 |
| K+ accumulate at one end of sieve plate creates a potential diff between sieve plate |
- water + dissolved compounds (in phloem sap)
- move + circulate together
- in one direction (in sieve tube)
- it’s slow + depends on metabolic energy/due to their kinetic energy.
- circulation slow down at sieve plate
- and forced out from cytoplasmicc streaming (thru pores)
- to cytoplasmic streaming of next sieve tube.
 |
| Circulation slow down at sieve plate |
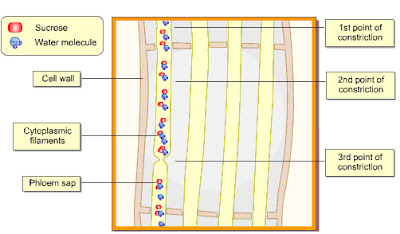
(D) In Peristaltic Wave Mechanism:
- sieve tube is filled with fine cytoplasmic filaments
- continuous from sieve tube to the next
- thru pores of sieve plate.
- contain phloem sap tube constrict + relax alternately
- pushing sap from one sieve tube to the next.
- constriction + relaxation/peristaltic movement form a pattern of wave = peristaltic wave
- can be at diff speed + in opposite direction (in sieve tube)
- depends on metabolic energy/ATP.
 |
| Phloem sap tube constrict + relax alternately |


No comments:
Post a Comment