- produce sperm + hormones
- under the influence of pituitary gonadotrophins, FSH +LH
- contains scrotum
- kept 2 °C <normal body temperature
- optimal for sperm production (spermatogenesis).
2. Ducts:
- vasa efferentia + vas deferens
-
transport sperm to urethra
3. Glands:
- prostate gland, Cowper’s gland,
seminal vesicles
- contribute fluid to semen.
4. Sperm (in seminal
fluid)
- discharged from body thru penis ( intromittent organ).
5. Each testis:
- consists
of about a thousand seminiferous tubules.
6. Each tubule:
- lined
by germinal epithelium
- which divides to give rise to sperm
- + two months.
1. Interstitial cells:
- between seminiferous tubules
- contain Leydig cells
- produce testosterone
- influence of LH (in pituitary gland).
2. Testosterone:
-
stimulates development + maintenance of male secondary sexual
characteristics + accessory sex organs.
characteristics + accessory sex organs.
3. Spermatogenesis:
-
starts at puberty
- when FSH stimulates series of cell divisions
- of germinal
epithelium
- of seminiferous tubules.
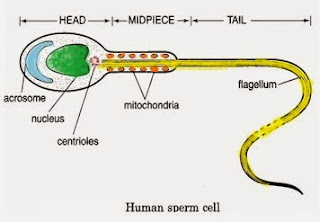
4. Spermatozoan cell:
- cytoplasm
disappeared during development.
5. Acrosome:
- large lysosome
- enzymes to digest
outer membranes of the egg (female gamete)
6. Mitochondria - provide energy
for locomotional flagella movement.
Human female reproductive system consists of:
1. Pair of ovaries:
- which produce ova
- carried by Fallopian tubes (oviductus)
- to uterus.
2. cervix - muscular ring at outer end of uterus.
3. vagina – opening to outside of body.
1. At birth:
- ovaries
contain about two million follicles
- which
started to divide by meiosis,
- but
stopped at prophase I (primary oocytes).
- subsequent
development at monthly intervals (menstrual cycle).
2. Oogenesis is regulated by the
pituitary hormones FSH + LH.
3. Ovulation +
development of secondary sexual characteristics
+ uterine changes in preparation for implantation of a fertilised egg
- controlled by the ovarian hormones (oestrogen + progesterone).
4. Fertilisation:
- occurs in the
Fallopian tubes
- and the zygote is transported to the uterus
- by the action of
cilia lining.
5. Development of the
zygote + embryo is viviparous