- made up of myosin molecule.
- has a long tail + double head (projects from filament’s surface).
- head - contains ATP binding site.
2. Thin actin filament made up of:
- two strands of globular actin protein (twisted together)
- regulatory proteins (troponin + tropomyosin).
3. When Ca2+ is not available:
- troponin + tropomyosin - block myosin binding sites (on actin filaments).
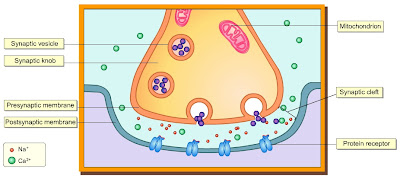
4. Muscular junction:
- specialised form of synapse
- found between motor neuron + sleletal muscle.
- spans across one unit of sarcomere.
5. Sarcolemma = postsynaptic membrane
6. Acetylcholine = transmitter substance (in synaptic vesicles).
7. Acetylecholine binding sites = located in the folds of the sacrcolemma
8. Calcium ions:
- found in abundance
- in sarcoplasmic reticulum.
9. T tubules = very closely associated with sarcoplasmic reticulum.
10. Nervous impulse:
è arriving at the neuromuscular junction
è generates action potential
è which spreads along sarcolemma.
11. Action potential:
è depolarises T tubule
è causing sarcoplasmic reticulum
è to release Ca2+ ions
è into sarcoplasm.
è allow actin + myosin filaments to interact.
12. ATP:
- provides energy needed
- to power the sliding + pulling motion
- between actin + myosin.
13. If Ca2+ ions + ATP conc. is sufficiently high à sequence will be repeated.